Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nemoto, Takahiro; Arakawa, Ryoki; Kawakami, Satoru; Nagasumi, Satoru; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Onishi, Takashi; Kawamoto, Taiki; Furusawa, Takayuki; Inoi, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-005, 33 Pages, 2023/05
During shut down of the HTTR (High Temperature engineering Test Reactor) RS-14 cycle, an increasing trend of filter differential pressure for the helium gas circulator was observed. In order to investigate this phenomenon, the blower of the primary helium purification system was disassembled and inspected. As a result, it is clear that the silicon oil mist entered into the primary coolant due to the deterioration of the charcoal filter performance. The replacement and further investigation of the filter are planning to prevent the reoccurrence of the same phenomenon in the future.
Matsushita, Kentaro; Ezure, Toshiki; Imai, Yasutomo*; Fujisaki, Tatsuya*; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/08
Development of evaluation method for cover gas entrainment (GE) by vortices generated at free surface in upper plenum of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) is required. GE evaluation tool, named StreamViewer, based on method using numerical results of three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics analysis for loop-type SFRs has been developed. In this study, modification of evaluation method of StreamViewer to rationalize conservativeness in evaluation results was examined by identifying vortex center lines and calculating three-dimensional distribution of pressure decrease along vortex center lines. The applicability of modified method was checked using water experimental result in rectangular open channel where unsteady vortices are generated. As the result, it was indicated that evaluation results on gas core depth which were excessive in current method were improved in modified method, and it is confirmed that modified method may discriminate onset of GE with appropriate criteria.
Torikawa, Tomoaki*; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Daisuke*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*; Matsushita, Kentaro; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki
Konsoryu, 36(1), p.63 - 69, 2022/03
On free surface of a sodium cooled fast reactor, gas entrainment can be caused by free surface vortices, which may result in disturbance in core power. It is important to develop an evaluation model to predict accurately entrained gas flow rate. In this study, entrained gas flow rate a simple gas entrainment experiment is conducted with focusing on effect of pressure difference between upper and lower tanks. Pressure difference between upper and lower tanks are controlled by changing gas pressure in lower tank. As a result, it is confirmed that the entrained gas flow rate increases with increasing pressure difference between upper and lower tanks. By visualization of swirling annular flow in suction pipe, it is also observed that pressure drop in suction pipe increases with increase in entrained gas flow rate, which implies that entrained gas flow rate can be predicted by evaluation model based on pressure drop in swirling annular flow region.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-006, 61 Pages, 2021/04
An experiment denoted as SB-PV-09 was conducted on November 17, 2005 using the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF) in the Rig of Safety Assessment-V (ROSA-V) Program. The ROSA/LSTF experiment SB-PV-09 simulated a 1.9% pressure vessel top small-break loss-of-coolant accident in a pressurized water reactor (PWR). The test assumptions included total failure of high pressure injection system and non-condensable gas (nitrogen gas) inflow to the primary system from accumulator (ACC) tanks of emergency core cooling system (ECCS). In the experiment, liquid level in the upper-head was found to control break flow rate. When maximum core exit temperature reached 623 K, steam generator (SG) secondary-side depressurization was initiated by fully opening the relief valves in both SGs as an accident management (AM) action. The AM action, however, was ineffective on the primary depressurization until the SG secondary-side pressure decreased to the primary pressure. Meanwhile, the core power was automatically reduced when maximum cladding surface temperature of simulated fuel rods exceeded the pre-determined value of 958 K to protect the LSTF core due to late and slow response of core exit temperature. After the automatic core power reduction, loop seal clearing (LSC) was induced in both loops by steam condensation on the ACC coolant injected into cold legs. The whole core was quenched because of core recovery after the LSC. After the ACC tanks started to discharge nitrogen gas, the pressure difference between the primary and SG secondary sides became larger. After the continuous core cooling was confirmed through the actuation of low pressure injection system of ECCS, the experiment was terminated. This report summarizes the test procedures, conditions, and major observations in the ROSA/LSTF experiment SB-PV-09.
Aihara, Jun; Goto, Minoru; Ueta, Shohei; Tachibana, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-018, 22 Pages, 2020/01
Concept of Pu-burner high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) was proposed for purpose of more safely reducing amount of recovered Pu. In Pu-burner HTGR concept, coated fuel particle (CFP), with ZrC coated yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) containing PuO (PuO
(PuO -YSZ) small particle and with tri-structural isotropic (TRISO) coating, is employed for very high burn-up and high nuclear proliferation resistance. ZrC layer is oxygen getter. On the other hand, we have developed Code-B-2.5.2 for prediction of pressure vessel failure probabilities of SiC-tri-isotropic (TRISO) coated fuel particles for HTGRs under operation by modification of an existing code, Code-B-2. The main purpose of modification is preparation of applying code for CFPs of Pu-burner HTGR. In this report, basic formulae are described.
-YSZ) small particle and with tri-structural isotropic (TRISO) coating, is employed for very high burn-up and high nuclear proliferation resistance. ZrC layer is oxygen getter. On the other hand, we have developed Code-B-2.5.2 for prediction of pressure vessel failure probabilities of SiC-tri-isotropic (TRISO) coated fuel particles for HTGRs under operation by modification of an existing code, Code-B-2. The main purpose of modification is preparation of applying code for CFPs of Pu-burner HTGR. In this report, basic formulae are described.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-003, 60 Pages, 2018/03
Experiment SB-PV-07 was conducted on June 9, 2005 using LSTF. Experiment simulated 1% pressure vessel top small-break LOCA in PWR under total failure of HPI system and nitrogen gas inflow to primary system from ACC tanks. Liquid level in upper-head was found to control break flow rate. Coolant was started to manually inject from HPI system into cold legs as first accident management (AM) action when maximum core exit temperature reached 623 K. Fuel rod surface temperature largely increased because of late and slow response of core exit temperature. SG secondary-side depressurization was initiated by fully opening relief valves as second AM action when primary pressure decreased to 4 MPa. However, second AM action was not effective on primary depressurization until SG secondary-side pressure decreased to primary pressure. Pressure difference became larger between primary and SG secondary sides after ACC tanks started to discharge nitrogen gas.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Takeda, Takeshi; Asaka, Hideaki; Nakamura, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 43(1), p.55 - 64, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.9(Nuclear Science & Technology)Effects of non-condensable gas from the accumulator tanks on secondary depressurization, as one of accident management (AM) measures in case of high pressure injection system failure, are studied at the ROSA-V/LSTF experiments simulating a ten instrument-tube break LOCA at the PWR vessel bottom. In an experiment with no gas inflow, the secondary depressurization at -55 K/h initiated by SI signal with 10 minutes delay succeeded in the LPI actuation. On the other hand, the gas inflow in another experiment degraded the primary depressurization and resulted in core uncovery before the LPI start. The third experiment with rapid secondary depressurization and continuous auxiliary feedwater supply, however, showed a possibility of long-term core cooling by the LPI actuation. RELAP5/MOD3 code analyses well predicted these experiment results and clarified that condensation heat transfer was largely degraded by the gas in the U-tubes. In addition, a primary pressure - coolant mass map was found to be useful for indication of key plant parameters of AM measures.
Hidaka, Akihide; Kudo, Tamotsu; Ishigami, Tsutomu; Ishikawa, Jun; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(12), p.1192 - 1203, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)An experimental program VEGA is being performed at JAERI to understand mechanisms of radionuclides release from fuel during severe accidents and to improve source term predictability. The VEGA tests showed that the Cs release rate at 1.0MPa decreased by about 30% compared with that at 0.1MPa. To explain this pressure effect, a numerical release model on 2-stage diffusion that considers the lattice diffusion in grains followed by gaseous diffusion in open pores was newly developed and a simplified model 1/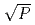 CORSOR-M was derived from the numerical model. The effect of pressure on source term was also estimated for a transient sequence at BWR with JAERI's THALES-2 code in which the simplified model was incorporated. Since the adequacy and applicability of 1/
CORSOR-M was derived from the numerical model. The effect of pressure on source term was also estimated for a transient sequence at BWR with JAERI's THALES-2 code in which the simplified model was incorporated. Since the adequacy and applicability of 1/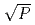 CORSOR-M model were confirmed for the pressures up to 16 MPa through comparison with the VEGA tests and mechanistic models, it is proposed that the model be used for source term analyses.
CORSOR-M model were confirmed for the pressures up to 16 MPa through comparison with the VEGA tests and mechanistic models, it is proposed that the model be used for source term analyses.
Otsuki, Ryusei*; Nasu, Shoichi*; Fujimori, Ryosuke*; Anada, Kinji*; Ohashi, Kentaro*; Yamamoto, Ryoichi*; Fujii, Kimio; Okubo, Keisuke*
Funtai Oyobi Fummatsu Yakin, 51(8), p.622 - 625, 2004/08
Effects of carbon materials on weight yield of (C +C
+C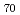 ) and weight ratios of C
) and weight ratios of C to (C
to (C +C
+C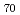 ) in soot were examined by the Joule resistive heating of four kinds of carbon materials at He gas pressures from 0.7
) in soot were examined by the Joule resistive heating of four kinds of carbon materials at He gas pressures from 0.7 10
10
 8.0
8.0 10
10 Pa for collector radii of 45, 50 and 55mm. The yields were in the range of 1 to 8% for graphite with hexagonal lattice, and better than those for glassy carbon. The most effective He gas pressure for the fullerene yield were in the range of 4.0
Pa for collector radii of 45, 50 and 55mm. The yields were in the range of 1 to 8% for graphite with hexagonal lattice, and better than those for glassy carbon. The most effective He gas pressure for the fullerene yield were in the range of 4.0 5.3
5.3 10
10 Pa. Any collector radii dependence of the yields was not observed. The weight ratios of C
Pa. Any collector radii dependence of the yields was not observed. The weight ratios of C to (C
to (C +C
+C ) were about 60 to 70%, and showed neither He gas pressure depenndennce nor collector radii depenndence four kinds of carbon materials.
) were about 60 to 70%, and showed neither He gas pressure depenndennce nor collector radii depenndence four kinds of carbon materials.
Furusawa, Takayuki; Sumita, Junya; Ueta, Shohei; Nemoto, Takahiro; Oyama, Sunao*; Kamata, Takashi
JAERI-Tech 2004-024, 46 Pages, 2004/03
Primary helium circulators of the HTTR are the important component as the helium gas which is reactor coolant, and three circulators for the primary pressurized water cooler and one for the intermediate heat exchanger are installed in primary cooling system. In the upstream of these circulators, the filter has been installed in order to suppress that it is entrapped in the bearing in which fine particles in helium gas, support main shaft of the helium circulator. The differential pressure of this filter rose gradually during rise-to-power test. The rise of the filter differential pressure of the helium circulator may cause the problem for reactor operation. Therefore, the filters were newly manufactured, and replacement of the filter was carried out. In replacement of the filter, appearance confirmation was carried out and deposit of the filter was analyzed. This paper described replacement of the filter and filter differential pressure rise investigation of the causes.
Yonomoto, Taisuke; Okubo, Tsutomu; Iwamura, Takamichi; Ishida, Toshihisa
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-11) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2003/04
An innovative concept of the pressure suppression system having functions of water injection and non-condensable gas confinement is developed for the next generation light water reactors (LWRs). The use of the system is advantageous for the mitigation of effects of the loss-of-coolant accidents (LOCAs) in (1) keeping the containment pressure as low as for the conventional LWRs, (2) injecting water to the containment for cooling the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) and/or flooding a break, and (3) confining the non-condensable gas in the drywell. The gas confinement function makes the system considerably suitable for reactor designs with passive cooling systems utilizing heat exchangers, such as the steam generator (SG) secondary side cooling system for an integral reactor, and the passive containment cooling system (PCCS), because it avoids adverse effects of non-condensable gas on the heat transfer performance during LOCAs. The usefulness of the developed concept is confirmed in the RELAP5/MOD3 code calculation.
Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Katanishi, Shoji; Takada, Shoji; Takizuka, Takakazu; Yan, X.; Nakata, Tetsuo; Takei, Masanobu; Kosugiyama, Shinichi; Shiozawa, Shusaku
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Dai-8-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.181 - 184, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
Hanada, Masaya; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Morishita, Takatoshi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Okumura, Yoshikazu; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 56-57, p.505 - 509, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:76.38(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Ueta, Shohei; Sumita, Junya; Tobita, Tsutomu*; Minato, Kazuo
Transactions of 16th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-16) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
*; J.Huang*; *; *; *; Yamaguchi, Kenji*; Sugimoto, Jun
JAERI-Tech 98-003, 32 Pages, 1998/02
no abstracts in English
*; A.M.Shehata*; Kunugi, Tomoaki; D.M.McEligot*
JAERI-Research 97-029, 36 Pages, 1997/03
no abstracts in English
*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; *; Nakamura, Hideo; ; Kukita, Yutaka
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 39(8), p.669 - 680, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Shimomura, Hiroaki
JAERI-Research 96-034, 73 Pages, 1996/06
no abstracts in English
Miyamoto, Naoki*; ; Okumura, Yoshikazu; Inoue, Takashi; Fujiwara, Yukio; Miyamoto, Kenji; Nagase, Akihito*; Ohara, Yoshihiro; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
AIP Conference Proceedings 380, p.300 - 308, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Kumamaru, Hiroshige; ; Murata, Hideo; Kukita, Yutaka; Akiyama, Mamoru*; *; *; *; *; *; et al.
Proc. of ASME JSME 4th Int. Conf. on Nuclear Engineering 1996 (ICONE-4), 1(PART B), p.669 - 674, 1996/00
JSME 4th Int. Conf. on Nuclear Engineering 1996 (ICONE-4), 1(PART B), p.669 - 674, 1996/00
no abstracts in English